WipeOut is an advanced security tool, which allows you to completely remove sensitive data from your hard drive.
It overwrites the data several times with carefully selected patterns, wiping the data completely. You can drag and drop files and folders into the WipeOut Bin, use the windows Explorer to WipeOut the Files, or WipeOut the Recycle Bin.

WipeOut securely and permanently erase unlimited files, folders and drives
Enterprise centralized console and remote WipeOut of data
Storage Analyzer intelligent utility to identify sensitive data on your endpoints and servers
Rescue me WipeOut your important files with one click
Schedule WipeOut of your data to meet your data retention and disposal policy needs
Certificate of destruction generate report of data wiping with all details for auditors
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLB)
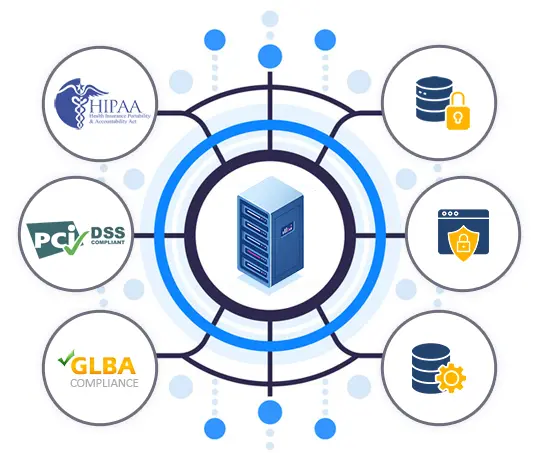
State Regulation of Protecting the Confidentiality of Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Organization Data Privacy and Security Guidelines
Organization Data Retention and Disposal Guidelines
WipeOut is an advanced security tool, which allows you to completely remove sensitive data from your hard drive.
Erase database records selectively with single click
Integrate permanent erasure functionality in your own applications using WipeOut API
Partnership with data centers and colo providers for sanitization on demand and as a service
This offering includes review of your data disposal policies, audit assistance for data disposal controls and implementation of WipeOut.
This product ensure your organization is meeting the standard put forth in the NIST 800-88, 800-36 Guidelines for Computer Security.
"Clearing information is a level of media sanitization that would protect the confidentiality of information against a robust keyboard attack. Simple deletion of items would not suffice for clearing. Clearing must not allow information to be retrieved by data, disk, or file recove ry utilities. It must be resistant to keystroke recovery attempts executed from standard input devices and from data scavenging tools. For example, overwriting is an acceptable method for clearing media".
"Overwriting. One method to sanitize media is to use software or hardware products to overwrite storage space on the media with non-sensitive data. This process may include overwriting not only the logical storage location of a file(s) (e.g., file allocation table) to be erased or permanently removed but also the entire media, including all addressable locations. The security goal of the overwriting process is to replace sensitive data with nonsensitive random data. Media should be overwritten a minimum of three times using a method based on the information sensitivity contained on the media. Overwriting cannot be used for media that are damaged or not rewritable. The media type and size may also influence whether overwriting is a suitable sanitization method".
WipeOut is an advanced security tool, which allows you to completely remove sensitive data from your hard drive.
It overwrites this data several times with carefully selected patterns, wiping the data correctly. You can drag and drop files and folders into the WipeOut Bin, use the windows Explorer to WipeOut the Files, or WipeOut the Recycle Bin.
WipeOut is a patented secure data erasure software that complies with global information security and privacy standards like GDPR, HIPPA, CCPA, NIST, ISO27001, DPDPA 2023 India, and more. It offers five different offerings: WipeOut Standalone, Enterprise (Server + Client Model), WipeOut Database, WipeOut API, WipeOut as a service, Data Sanitization, and Assistance Program. WipeOut generates a certificate of data erasure as per the NIST data sanitization guidelines. It has features like selective file/folder/drive erasure, scheduler for scheduling erasure, rescue me for emergency one-click wipe, and storage analyzer.
WipeOut offers five different offerings:
WipeOut has several features, including:
WipeOut complies with several global information security and privacy standards, including:
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a non-regulatory agency of the United States Department of Commerce. NIST develops and issues standards, guidelines, and other publications to assist federal agencies in implementing the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) and to help private sector organizations in protecting their information systems. WipeOut generates a certificate of data erasure which is as per the NIST data sanitization guidelines.
WipeOut Standalone is a single-user software that can be installed on a single computer. WipeOut Enterprise, on the other hand, is a server-client model that can be installed on multiple computers and managed centrally.
WipeOut Database is a specialized offering that is designed to erase data from databases. It supports several popular database management systems like MySQL, and Microsoft SQL Server.
WipeOut API is a software development kit (SDK) that allows developers to integrate WipeOut’s data erasure capabilities into their own applications.
The Data Sanitization and Assistance Program is a service offered by WipeOut that provides assistance with data erasure. It includes services like data analysis, data classification, and data erasure.
The Rescue Me feature in WipeOut is designed to help users in emergency situations. It allows users to erase all data on their computer with a single click, without having to go through the usual data erasure process.
The Scheduler feature in WipeOut allows users to schedule data erasure at a specific time. This is useful for organizations that need to erase data on a regular basis.
With growing data leakages due to traditional, inadequate data deletion procedures in organizations, more and more regulations now enforce use of WipeOut data erasure techniques (secure overwriting algorithms) to ensure compliance.
Data discovery and scheduled erasure policies across organization
“WipeOut” integrated into windows as a widget with drag/drop functionality
Rescue Me (unique feature that allows erasure of important files at one click)
Erasure of selective database records (offered as database WipeOut version)
WipeOut for lost/stolen assets
Enterprise Server/Client data erasure policy management
Certificate of Data Erasures for audit trails
Remote WipeOut

The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)

The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)

Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLB)
State Regulation of Protecting the Confidentiality of Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Organization Data Privacy and Security Guidelines
Organization Data Retention and Disposal Guidelines
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLB)

State Regulation of Protecting the Confidentiality of Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Organization Data Privacy and Security Guidelines
Organization Data Retention and Disposal Guidelines

"Clearing information is a level of media sanitization that would protect the confidentiality of information against a robust keyboard attack. Simple deletion of items would not suffice for clearing. Clearing must not allow information to be retrieved by data, disk, or file recove ry utilities. It must be resistant to keystroke recovery attempts executed from standard input devices and from data scavenging tools. For example, overwriting is an acceptable method for clearing media".
"Overwriting. One method to sanitize media is to use software or hardware products to overwrite storage space on the media with non-sensitive data. This process may include overwriting not only the logical storage location of a file(s) (e.g., file allocation table) to be erased or permanently removed but also the entire media, including all addressable locations. The security goal of the overwriting process is to replace sensitive data with nonsensitive random data. Media should be overwritten a minimum of three times using a method based on the information sensitivity contained on the media. Overwriting cannot be used for media that are damaged or not rewritable. The media type and size may also influence whether overwriting is a suitable sanitization method".
It overwrites this data several times with carefully selected patterns, wiping the data correctly. You can drag and drop files and folders into the WipeOut Bin, use the windows Explorer to WipeOut the Files, or WipeOut the Recycle Bin.
